Knee Ligament Injury
The knee, a remarkable joint in the human body, comprises several vital components working together seamlessly. Our expert medical team includes sport medicine and orthopedic surgeons who specialize in knee injury treatment.
At its core are the ligaments, robust bands of connective tissue that stabilize and support the joint. To understand the intricacies of knee ligament injuries, we must first explore the distinct parts of this joint and their functions.
Exploring the Knee Ligaments
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
The ACL, located in the center of the knee, is crucial for preventing the shinbone from moving too far forward. It stabilizes the joint during movements like pivoting and sudden stops.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
Situated near the ACL, the PCL prevents the shinbone from moving backward excessively. It plays a vital role in maintaining knee stability.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
Positioned on the inner side of the knee, the MCL safeguards against excessive inward bending. It provides crucial stability for lateral movements.
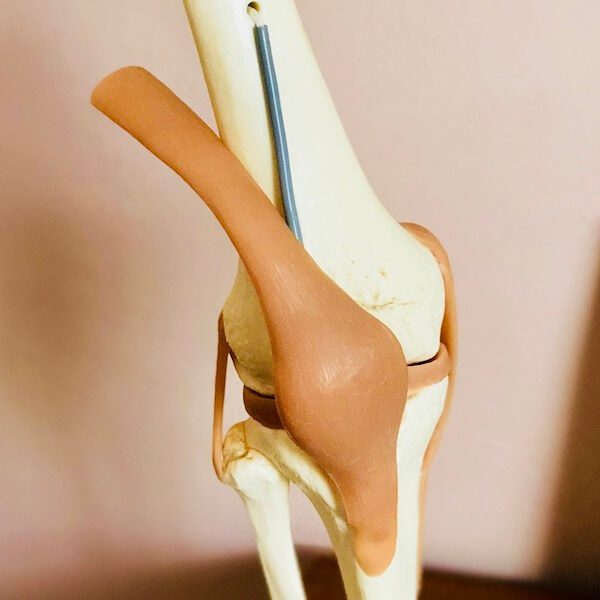
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)
The LCL, found on the outer knee, restricts excessive outward bending, providing stability for lateral movements.
Common Injuries to Knee Ligaments
Each of these knee ligaments is susceptible to particular injuries, often resulting from sports activities or accidents.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
The ACL is commonly injured during activities involving sudden stops, direction changes, or pivoting, such as soccer or basketball. Tears to the ACL can be partial or complete.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
PCL injuries typically occur when there's a forceful blow to the knee, often seen in car accidents or sports-related collisions.
Medial Collateral Ligament Injury
MCL injuries often happen due to direct impact to the outer knee or excessive force causing inward bending. Sports like football or skiing can lead to MCL sprains or tears.
Lateral Collateral Ligament Injury
LCL injuries are less common but can result from sudden outward bending, often seen in contact sports or accidents.
Collateral Ligaments Injury
A collateral ligament injury involves damage to the ligaments on the sides of the knee joint. These injuries often occur due to sudden impacts or forceful blows to the knee, such as those experienced in sports or accidents.
MEET OUR SPORTS MEDICINE & ORTHOPEDICS TEAM
- All
- Sports Medicine
- Orthopedic

Ligament Injury is Serious
Understanding these injuries is essential, but equally crucial is knowing that knee ligament injuries should be diagnosed and treated by medical experts like orthopedic surgeons. Seeking professional care ensures accurate assessment and appropriate treatment.
Moreover, preventative measures, including strength and conditioning exercises tailored to the knee's unique requirements, can reduce the risk of ligament injuries. These exercises strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing additional support and stability.
Understanding Knee Ligament Injury
Injuries to knee ligaments can be both painful and debilitating, affecting one's ability to perform daily activities or engage in sports. Having a knee ligament injury diagnosed properly is a crucial first step in addressing these injuries effectively, it's crucial to comprehend the various types of torn knee ligament injuries, their causes, and the treatment options available.
Types of Torn Knee Ligament Injuries
Anterior Cruciate Ligament ACL Injuries
ACL injuries are prevalent among athletes and typically occur during activities that involve sudden stops, pivoting, or changes in direction. These injuries can range from mild sprains to complete tears, often causing instability and swelling in the knee.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injuries
PCL injuries are less common than ACL injuries and usually result from a forceful blow to the knee when it's bent. They can vary in severity, leading to symptoms like pain, swelling, and instability.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injuries
MCL injuries often happen due to a direct impact on the outer knee or excessive force causing the knee to bend inward. They can result in varying degrees of damage, from minor sprains to complete tears, and lead to pain and difficulty moving the knee.
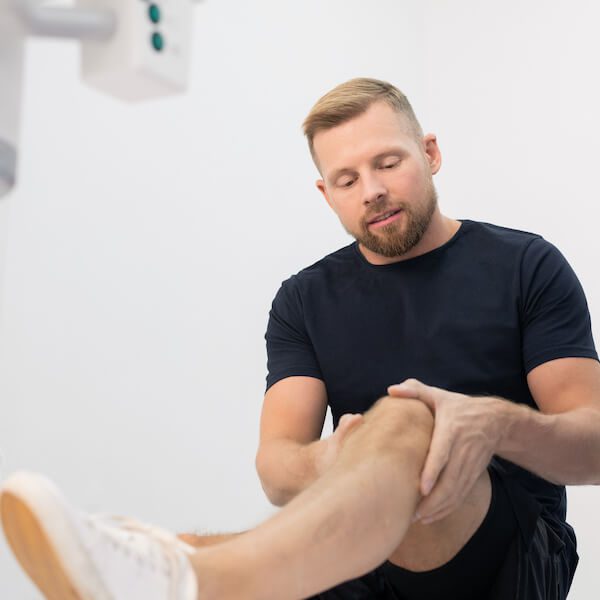
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injuries
While less frequent than other ligament injuries, LCL injuries can occur when there's forceful bending of the knee outward. This type of injury can cause pain, swelling, and instability.
Traditional Treatment Options
Historically, treatment for knee ligament injuries often involved conservative measures like rest, physical therapy, and bracing. However, these approaches didn't always provide optimal outcomes, particularly for severe tears. Recently a growing number of articles and research papers have shown that some types of ACL tears can be treated non-surgically.
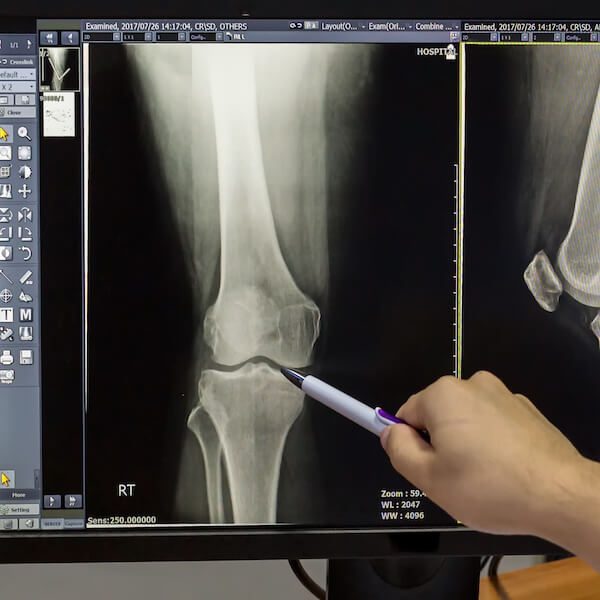
For more serious cases, surgical intervention was necessary. Surgical options included ligament reconstruction, where the damaged ligament is replaced with a graft, often from a tendon in the patient's own body or a donor source.
In recent years, advances in medical technology and surgical techniques have greatly improved the management of knee ligament injuries. At Valiant Clinic & Hospital, our team of sports medicine and orthopedic experts offers cutting-edge treatments that are tailored to the specific type and severity of the injury. This ensures that patients receive the most effective care and have the best chances of a full recovery.
Understanding the Functions of Each Ligament Type
To truly grasp the significance of knee ligament injuries, it's essential to comprehend the distinct functions of each knee ligament. The knee is a complex joint with four primary ligaments, and each plays a crucial role in maintaining stability and facilitating movement.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
The ACL is perhaps the most well-known knee ligament. It runs diagonally through the center of the knee, connecting the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). Its primary function is to prevent excessive forward movement of the tibia in relation to the femur and control rotational movements of the knee. This ligament is particularly vulnerable to injury during activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or landing from a jump.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
The PCL, located at the back of the knee, also connects the femur to the tibia. Its primary role is to prevent the tibia from moving too far backward in relation to the femur. PCL injuries often occur due to a direct blow to the front of the knee when it's bent, such as in a car accident or sports-related collision.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
The MCL is found on the inner side of the knee and connects the femur to the tibia. Its primary function is to provide stability by preventing the knee from bending inward. MCL injuries typically happen when there's a blow to the outer knee, forcing it to bend inward. This can occur during contact sports or traumatic accidents.
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)
The LCL runs along the outer side of the knee, connecting the femur to the fibula (a bone in the lower leg). It plays a vital role in preventing the knee from bending outward. LCL injuries, though less common, can result from a forceful impact that pushes the knee inwards.
Understanding the specific functions of these ligaments helps illustrate why injuries to them can have a significant impact on an individual's mobility and overall knee stability. When one or more of these ligaments is damaged, it can lead to pain, swelling, and, most critically, instability in the knee joint.
The Impact of Knee Ligament Injuries and Strengthening Solutions
Knee ligament injuries, if left unaddressed, can have far-reaching consequences on an individual's life. Understanding the severity of such injuries and the importance of early diagnosis is crucial.
Injuries to knee ligaments, especially the ACL, can lead to instability in the knee joint. This instability makes it challenging to engage in everyday activities, let alone sports or physical fitness routines. A knee with ligament damage is more susceptible to recurrent injuries and can lead to long-term joint problems such as osteoarthritis.
Diagnosing these injuries promptly by a medical expert, such as an orthopedic surgeon, is of paramount importance. Medical professionals can accurately assess the extent of the injury using physical examinations and advanced imaging techniques like MRI scans. This diagnosis forms the foundation for creating a tailored treatment plan.
Preventing knee ligament injuries is equally crucial. Strengthening the knee through specific exercises can significantly reduce the risk of these injuries occurring in the first place. Whether you're an athlete or simply aiming to maintain an active lifestyle, these exercises can enhance knee stability:
Quad Sets: Contract your thigh muscles while sitting with your legs extended.
Straight Leg Raises: Lift your leg while keeping it straight.
Wall Slides: Lean against a wall and slide down into a seated position, then back up.
Hamstring Curls: While lying on your stomach, bend your knee by bringing your heel towards your buttocks.
Step-ups: Step onto a low stool or step, then back down.
Balancing Exercises: Stand on one leg, gradually increasing the duration as your balance improves.
Resistance Band Exercises: Utilize resistance bands for various leg exercises to build strength.
Remember, these exercises should be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a qualified physical therapist, especially if you've had a previous knee injury. Even after completing physical therapy, getting active again should be a process managed by a professional such as an injury rehabilitation personal trainer.
In addition to preventive measures, proper rehabilitation following a knee ligament injury is essential. At Valiant Clinic and Hospital, our sports medicine and orthopedic teams are experts in diagnosing and treating such injuries. Our personalized rehabilitation programs, designed to suit individual needs, ensure a comprehensive approach to recovery.
Comprehensive Treatment Options for Knee Ligament Injuries
At Valiant Clinic and Hospital, we understand the unique nature of knee ligament injuries and offer a comprehensive range of treatment options. Our multidisciplinary approach, involving sports medicine and orthopedic specialists, ensures that you receive the most effective care tailored to your specific needs.
Let's explore the various treatment modalities available for knee ligament injuries:
Non-Surgical Options:
Rest and Physical Therapy:
In many cases, mild knee ligament injuries can be managed non-surgically. Resting the injured knee and undergoing physical therapy can aid in healing and strengthening the surrounding muscles.
Bracing and Support:
The use of knee braces or supports can provide stability to the injured ligament during the healing process.
Medications:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Interventions:
Arthroscopy: For certain ligament injuries, minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery may be recommended. This procedure involves small incisions through which a tiny camera and surgical instruments are inserted to repair or reconstruct the damaged ligament.
Ligament Repair: In some cases, particularly with partial ligament tears, the damaged ligament can be repaired surgically.
Ligament Reconstruction: When a ligament is severely torn or cannot be repaired, a reconstruction procedure may be performed. This involves using graft tissue from your body or a donor to create a new ligament.
Our team of highly skilled orthopedic surgeons and sports medicine specialists will carefully evaluate your condition to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. We take into account factors such as the type and severity of the injury, your age, activity level, and overall health to make informed recommendations.
After the initial treatment phase, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in your recovery. Our physiotherapy department is staffed with experienced therapists who specialize in knee injury rehabilitation. They will guide you through a structured program aimed at restoring strength, flexibility, and function to your knee.
Moreover, we offer the option to work with a recommended injury rehabilitation personal trainer who can tailor exercises to your specific needs and goals. This personalized approach ensures that you regain confidence in your knee's stability and function.
Safeguarding Your Knee Health
In the journey of understanding knee ligament injuries, we've delved into the intricate structure of the knee and how each ligament functions. We've explored the common injuries that affect these ligaments and the circumstances that lead to their vulnerability.
The takeaway from this exploration is clear: your knee ligaments are vital for stability and mobility. Protecting them is crucial for maintaining an active and pain-free lifestyle.
Here are the key points to remember:
Early Diagnosis is Vital:
If you suspect a knee ligament injury, seek medical attention promptly. Timely diagnosis and intervention can prevent further damage and enhance the chances of a successful recovery.
Strength Through Rehabilitation:
Whether you've suffered a mild or severe injury, rehabilitation is essential. Physiotherapy and personalized exercises can rebuild strength and flexibility, aiding in the healing process and reducing the risk of re-injury.
Comprehensive Treatment at Valiant:
At Valiant Clinic and Hospital, we offer a wide range of treatment options, from non-surgical approaches to advanced surgical interventions. Our expert teams in sports medicine and orthopedics are here to guide you through every step of your recovery journey.
Embrace Prevention:
Protecting your knees from injuries is equally important. Maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee, and use proper techniques during physical activities to minimize the risk of injury.
Quality of Life:
Your knee health impacts your overall quality of life. Don't let knee pain or instability hold you back from the activities you love. With the right care and support, you can regain full function and mobility.
